NITROGEN (N)
NITROGEN: It is vital for plants. It is the building block of proteins, hormones, chlorophyllin, v, tamine, enzymes and many other phenomena you can think of. It is of great importance in the growth of the green part called vegetative part.
WHAT ARE THE NATURE SOURCES OF NITROGEN?
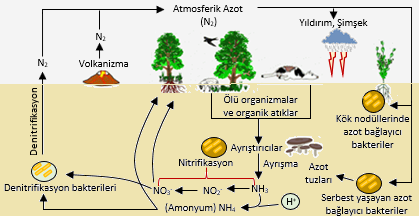
• Nitrogen, which is included in the structure of amino acids and proteins, nucleic acids, hormones and vitamins that form the building blocks of all living things, is one of the basic nutrients for life. The main source of nitrogen in nature is the atmosphere and nitrogen gas constitutes about 78.8% of the atmosphere. Plants and most organisms cannot use free nitrogen in the atmosphere as nutrients. For this, nitrogen has to go through various processes. These important processes in the nitrogen cycle are fixation, ammonification, nitrification, denitrification, mineralization and assimilation.
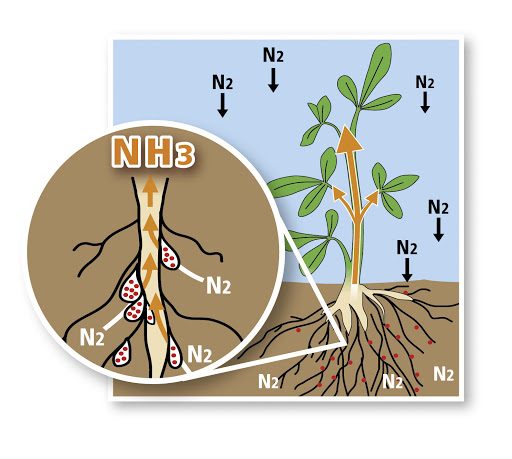
• nitrogen fixation; The conversion of nitrogen gas into nitrates and nitrites by atmospheric, biological and industrial processes is called nitrogen fixation. 12% of the fixation processes are bound to the soil by atmospheric fixation, 59% by biological fixation, and 29% by artificial fixation (manure fertilizer production).
• The first form of nitrogen that occurs when a plant or animal dies or when an animal defecates is organic. Bacteria and/or fungi convert the organic nitrogen in the residues to ammonium. The derivation of ammonium ions from organic compounds is called ammonification.
METHODS OF TAKING NITROGEN FROM PLANTS
Plants take up nitrogen in two forms. in the form of nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. the roots of the plant can easily take up these two nitrogen sources. Plants generally prefer nitrate nitrogen to ammonium nitrogen, but the rate of loss in soil is higher than nitrate nitrogen to ammonium nitrogen. Plants convert ammonium nitrogen to nitrate nitrogen by bacteria in the process called nitrification described above. Soil temperature is effective in this conversion. It takes place more quickly over 8 degrees to 9 degrees.
The soil pH at which nitrification is most effective is between 5.5 and 6.5. The nitrification process can take between 15 and 30 days.
ARE THERE LOSSES OF NITROGEN, IF THERE ARE WHAT?
Yes, there are nitrogen losses, many factors prevent plants from getting nitrogen. These factors are;
nitrate and ammonium nitrogens are converted to organic nitrogens, this process is called immobilization. In environments where water shortage and pH are high, ammonium nitrogen (NH4) turns into ammonium (NO3), which is a volatile gas, and ammonium gas evaporates into the atmosphere.
The importance of pH * You can learn about the importance of water by clicking on the importance of water in nature.
One of the other and important factors is that the fertilizers are washed away and go to deeper parts of the soil and remain in places where the plant roots cannot reach. excessive precipitation and flood irrigation (also called wild irrigation) is seen at a high rate * you can get information by clicking the irrigation link
Another loss is the dinitrification event that we mentioned in the nitrogen resources section in nature. As a result of this event, nitrate nitrogen (NH3) is converted to nitrite nitrogen (no4) with the help of bacteria and nitrite nitrogen is converted to nitrite oxide (NO). In the final stage, it turns into nitrogen gas and is released from the soil to the air.
There are losses as a result of its use by micro-organisms. Organic matter is decomposed by micro-organisms and the nitrogen formed as a result of decomposition is used by these organisms and the plant is prevented from taking it. For that matter, it is necessary to have high organic matter values in the soil. Unfortunately, the organic ratios of the soils in our country have decreased as a result of incorrect fertilization and have become quite inadequate. It is known that the organic matter values can be increased with the plant nutritional supplements to be used and the soil is reformed.